Automating Trust: Secure Firmware Lifecycle Management
Published on July 28, 2025,
by
The Importance of Secure Firmware Management
Edge computing and IoT are growing fast. Firmware security is now more critical than ever. Firmware controls hardware and runs below the operating system. If compromised, attackers gain deep, persistent access to devices. This makes firmware a top target for cyber threats.
Common Firmware Security Gaps
Despite its importance, firmware is often overlooked. Updates are delayed, protections are weak, and manual processes dominate. To secure edge deployments, automation is essential. Organizations need secure firmware lifecycle management from development to response.
The Criticality of Timely and Secure Firmware Updates
Firmware updates are essential. They patch security flaws and improve performance or features. Many vendors delay patches for months or longer. Outdated firmware leaves devices exposed to threats. Manual updates don’t scale in large edge environments. Automated Firmware-Over-the-Air (FOTA) updates are now essential.
Best Practices for Secure Firmware-Over-the-Air (FOTA) Updates
A secure FOTA process must ensure authenticity, integrity, and confidentiality. Key best practices include:
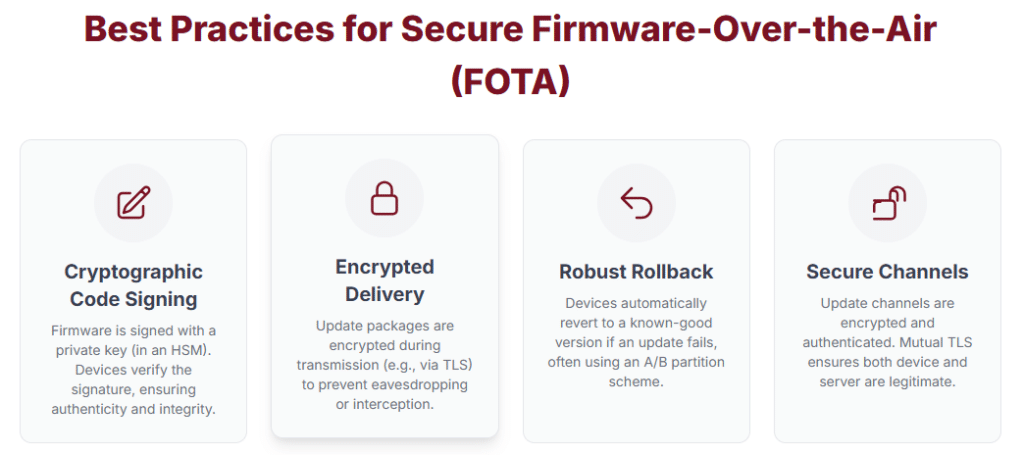
Cryptographic Code Signing
Firmware updates must be signed using a private key stored in a Hardware Security Module (HSM). Devices verify signatures using the vendor’s public key. This ensures updates are authentic and have not been tampered with.
Encrypted Delivery
Firmware update packages must be encrypted during transmission. Protocols like TLS prevent attackers from intercepting or analyzing the data.
Robust Rollback Capability
Devices should support automatic rollback to a stable firmware version. A/B partitioning helps recover from failed or unstable updates.
Secure and Authenticated Channels
Update channels must be encrypted and authenticated. Mutual TLS confirms both device and server identities during updates.
Automating Patch Management Across a Distributed Fleet

Managing firmware updates across many devices requires automation. Nlyte’s Device Management platform provides centralized control and visibility. It supports secure firmware lifecycle management across large deployments.
Key capabilities include:
- Centralized Policy Management: Define which devices get updates and when. Policies ensure updates follow organizational rules and schedules.
- Device Discovery and Inventory: Track firmware versions and patch status in real time. Maintain visibility across the entire device fleet.
- Phased Rollouts: Deploy updates to test groups first. Monitor performance before expanding to all devices.
- Automated Verification and Reporting: Track update success and failures automatically. Generate alerts and reports for compliance and auditing.
With Nlyte, organizations automate firmware updates confidently. This reduces risk and improves operational efficiency across distributed environments.
Leveraging Blockchain for Firmware Integrity Verification
Blockchain can enhance firmware trust and integrity across distributed environments. Organizations use distributed ledgers to verify firmware authenticity.
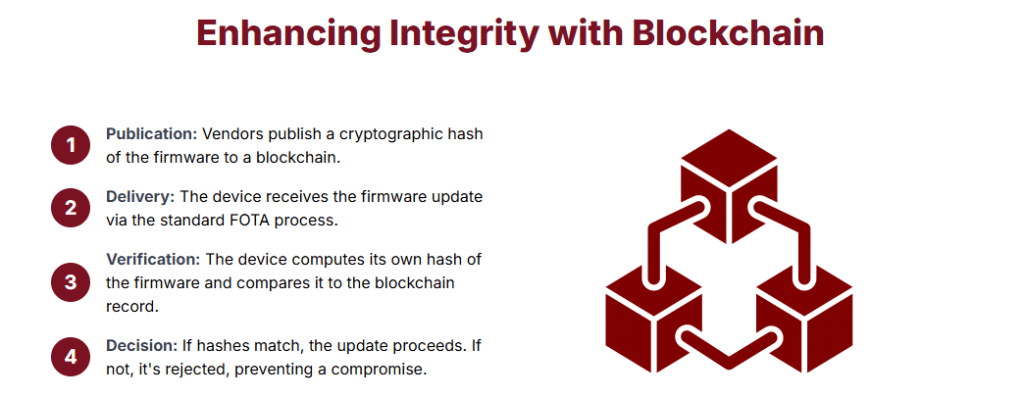
How It Works:
- Publication: Vendors publish a cryptographic hash of firmware to a blockchain.
- Delivery: Devices receive firmware via standard FOTA methods.
- Verification: Devices compute a hash and compare it to the blockchain record.
- Decision: If hashes match, update proceeds. If not, the update is rejected.
This decentralized model removes reliance on the update server. Devices verify authenticity using a public, immutable blockchain record. It protects against man-in-the-middle attacks and supports auditability.
Developing a Robust, Automated Incident Response Plan
Even strong protections can fail. A solid incident response plan must be built into edge management platforms.
Key Actions:
- Automated Quarantine: Immediately isolate compromised devices to prevent further damage.
- Forced Re-imaging: Push clean firmware to overwrite malicious code and restore functionality.
- Forensic Data Collection: Gather logs and evidence for analysis and investigation.
- High-Priority Alerting: Notify security teams with detailed incident data for fast response.
Automation ensures fast containment and recovery. It reduces damage and minimizes downtime across distributed environments.
A Checklist for Implementing a Secure FOTA Update Process
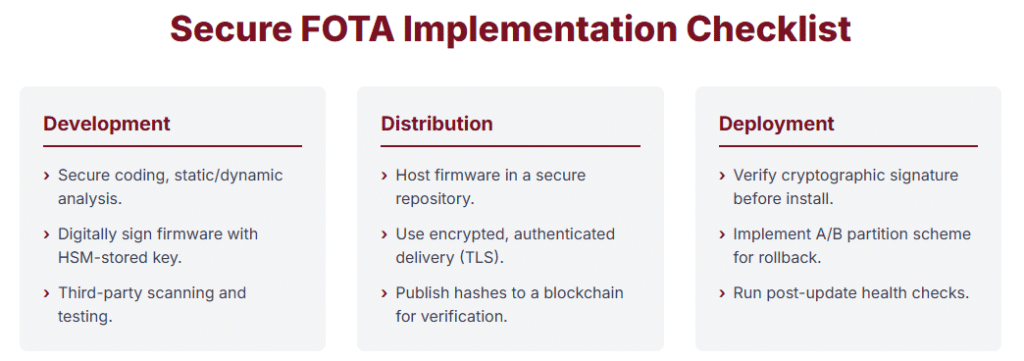
| Process Stage | Key Action / Control | Rationale / Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Development | Secure coding, static/dynamic analysis | Identify vulnerabilities early |
| Digitally sign firmware with HSM-stored key | Ensure authenticity and integrity | |
| Third-party scanning and testing | Independent security validation | |
| Distribution | Host firmware in secure repository | Prevent unauthorized modifications |
| Encrypted, authenticated delivery (TLS) | Protect update in transit | |
| Publish hashes to blockchain | Enable decentralized verification | |
| Deployment | Verify cryptographic signature | Final check before installation |
| A/B partition scheme | Enable rollback and resilience | |
| Post-update health checks | Detect and halt problematic rollouts |
Final Thoughts: Building Trust Through Automation
Firmware security is a continuous process, not a one-time task. Each stage must include cryptographic protections and automation. Decentralized verification adds another layer of trust and resilience.
Edge devices are everywhere in today’s connected world. Trust must be built into every update and every process. Automation is essential for maintaining security and reliability. It’s not just the key, it’s the future.
Strengthen Data Center Security with Nlyte’s Device Management Solution
