Power Up Your IQ: Smart vs. Dumb PDUs
Published on May 14, 2025,
by
Understanding PDUs: Intelligent vs Basic PDU Comparison
Think of a PDU as an industrial-grade power strip designed for the data center rack. Its fundamental job is to deliver reliable power to your critical IT equipment. But not all PDUs are created equal. The choice between a "Dumb" and a "Smart" PDU has massive implications for efficiency, cost, and uptime.
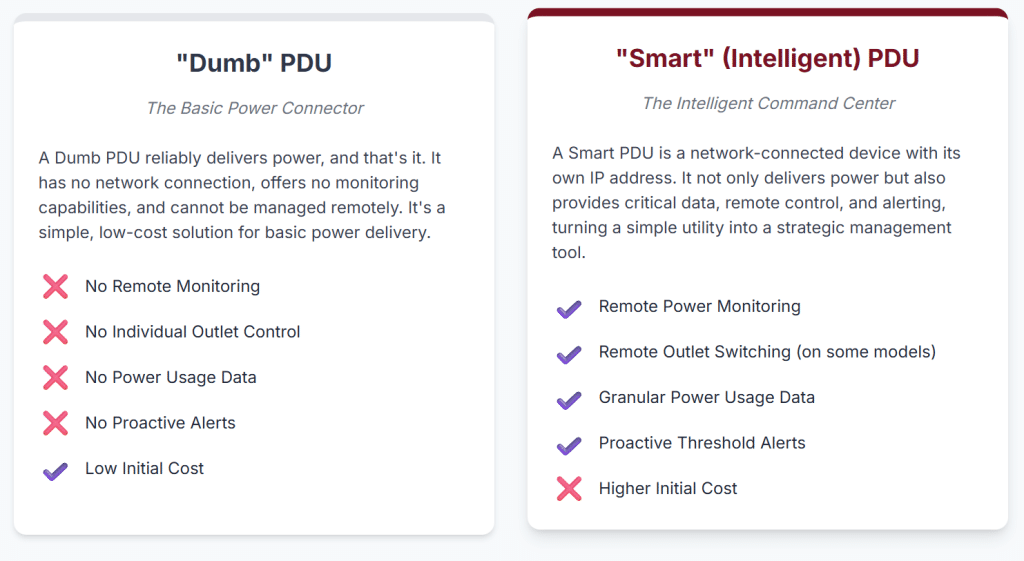
To appreciate the security challenges associated with data center power infrastructure, it is essential to understand the diverse types of PDUs and how their functionalities correlate with potential vulnerabilities. PDUs can be broadly categorized based on their intelligence and management capabilities, with each category presenting a distinct risk profile.
- Basic PDUs: These are the simplest form of power distribution, robust power strips designed for use in critical environments. They distribute power from a single input to multiple outputs but lack any form of metering, monitoring, or remote management capabilities. From a cybersecurity perspective, their risk is minimal and primarily confined to physical tampering, as they typically have no network connectivity.
- Metered PDUs: Metered PDUs provide the ability to monitor power consumption at the PDU level. This information, such as voltage, current, and power (kW), is typically displayed on a local digital meter. Some advanced metered PDUs may offer remote viewing of this aggregate data via a network connection, introducing a minimal level of network exposure and associated risks if not properly secured.
- Switched PDUs: Switched PDUs build upon metered PDU functionality by adding the capability to remotely control individual outlets. This allows administrators to power cycle equipment, turn outlets on or off, and schedule power sequences remotely. This remote-control feature inherently requires network connectivity and a more sophisticated management interface, thereby increasing the attack surface and the potential for unauthorized access or denial of service.
- Intelligent PDUs (iPDUs) / Smart PDUs: These are the most advanced types of PDUs, offering comprehensive remote monitoring and control down to the individual outlet level. They often integrate environmental sensors for temperature, humidity, and airflow, and provide detailed analytics and reporting capabilities. iPDUs are effectively networked embedded systems, possessing their own operating systems, firmware, and various network management interfaces (e.g., Web GUI, SNMP, SSH, Telnet, REST APIs). This complexity, while providing significant operational advantages, makes them the most susceptible to cyber vulnerabilities. Flaws in their embedded software, insecure default configurations, weak authentication mechanisms, or vulnerabilities in network protocols can be exploited by attackers.
Security Risks in the Intelligent vs Basic PDU Comparison
| PDU Type | Key Management Features | Network Connectivity (Protocols) | Primary Cyber Security Risks | Key Mitigation Approaches |
| Basic PDU | None; simple power distribution. | No | Physical tampering only. | Physical access control. |
| Metered PDU | Local PDU-level power display; some offer remote PDU-level monitoring. | Optional (e.g., Ethernet - SNMP, HTTP for some models) | Limited; unauthorized viewing of aggregate power data if remote access is insecure. | Secure remote access if used (strong credentials, network segmentation); regular firmware updates. |
| Switched PDU | PDU-level monitoring; remote on/off control of individual outlets; power sequencing. | Yes (e.g., Ethernet - SNMP, HTTP/HTTPS, SSH, Telnet) | Moderate; unauthorized outlet control (power cycling /shutdown), insecure remote access leading to DoS. | Strong authentication, network segmentation, disabling unused services (e.g., Telnet), use of encrypted protocols (HTTPS, SSH), regular firmware updates. |
| Intelligent PDU (iPDU) | Outlet-level power monitoring & control; environmental sensing; advanced alerting; DCIM integration; local display. | Yes (e.g., Ethernet - SNMPv3, HTTPS, SSH, REST APIs, RADIUS/LDAP) | High; unauthorized access leading to full control (power manipulation, configuration changes), RCE, DoS, data leakage, network pivot point. | Comprehensive security: strong authentication (MFA, centralized auth), RBAC, encryption, network segmentation/firewalling, regular vulnerability scanning and patching, secure firmware, disabling unused services, secure default configurations, audit logging. |
.
Choosing the Right Fit: Intelligent vs Basic PDU Comparison Insights
If your data center is already leveraging Intelligent PDUs, you're on the right path to gaining deeper visibility and control over your power infrastructure. But to truly maximize the value of these smart devices, it's essential to manage them proactively—especially when it comes to firmware updates.
That’s where Nlyte’s Device Management Solution comes in. This powerful tool is purpose-built to help data center teams centrally manage, monitor, and automate firmware updates across a wide range of intelligent devices, including PDUs. By using Nlyte’s solution, you can:
- Ensure firmware consistency across all your PDUs to reduce vulnerabilities and improve performance.
- Automate update processes to minimize manual effort and human error.
- Gain real-time visibility into device status and update compliance.
- Reduce downtime risks by keeping your infrastructure secure and up to date.
In short, if you’re using Intelligent PDUs, pairing them with Nlyte’s Device Management Solution is a smart move to ensure your infrastructure remains secure, efficient, and future-ready.
