Boosting Cooling Efficiency in Data Centers
Published on May 23, 2023,
by
As data centers grow in complexity and density, optimizing energy use becomes critical. One of the most impactful strategies is improving data center cooling efficiency. By leveraging airflow management, monitoring temperature differentials like Delta T, and adopting intelligent cooling technologies, operators can reduce energy waste, eliminate hotspots, and support long-term sustainability goals
Advanced HVAC Systems
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems are integral to maintaining optimal temperatures within data centers, and upgrading these systems can result in significant energy savings. Advanced HVAC systems are designed to minimize energy consumption by making use of the latest innovations in cooling technology.
- High-Efficiency Chillers: Traditional chillers can consume a significant amount of energy. High-efficiency chillers, on the other hand, are designed to maximize cooling capacity while minimizing energy use. These chillers utilize variable speed drives, magnetic bearing technology, and advanced heat exchangers to provide superior performance.
- Free Cooling Chillers: Also known as economizer systems, these take advantage of cool outside air or water to reduce the need for mechanical cooling. When conditions allow, free cooling chillers can dramatically cut energy usage and operational costs by bypassing the refrigeration cycle entirely.
- Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): VFDs control the speed of the motors in HVAC systems, allowing them to adjust to the precise cooling demand rather than running at full speed constantly. By adjusting the fan speed to match the current load, VFDs can significantly reduce energy consumption and improve overall system efficiency.
- Advanced Controls: Many modern HVAC systems come with advanced control systems that use sensors and algorithms to optimize cooling performance. These controls can adjust system operations based on a variety of factors, including the temperature of the air entering and leaving the server racks, the humidity level, and the outdoor weather conditions.
- Precision Cooling Units: Unlike traditional air conditioning units, precision cooling units are designed specifically for data centers. They provide precise temperature and humidity control, operate efficiently at higher return air temperatures, and have a higher sensible heat ratio (SHR), which is more suitable for data center environments.
Integrated Data Center Management (IDCM)
Integrated Data Center Management (IDCM) is an overarching approach to monitor, control, and optimize the various subsystems and processes within a data center. IDCM merges the management of IT and facilities infrastructure, enabling data center managers to have comprehensive, real-time insights into the state of their data center from a single, unified platform.
Components of an IDCM system can include:
- Real-time monitoring and alerts: IDCM tools can continuously monitor a wide range of parameters, including temperature, humidity, airflow, and power consumption across the data center. They can alert operators to any issues that might affect cooling efficiency or threaten equipment safety.
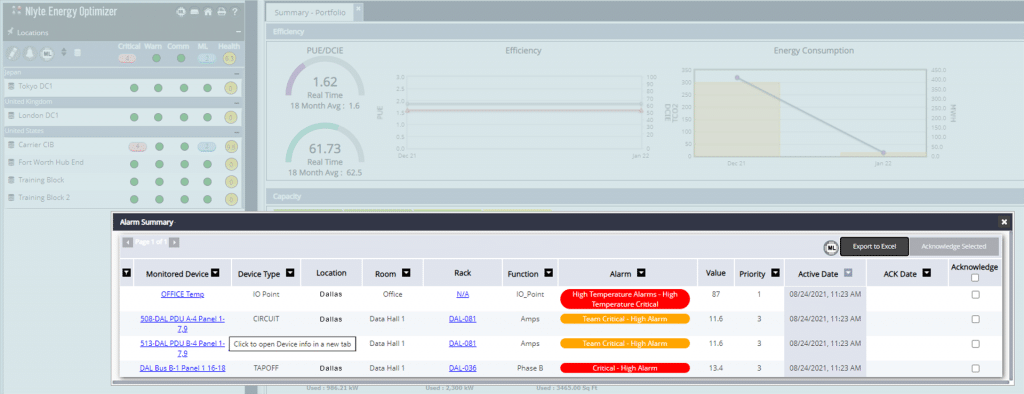
- Predictive analytics: Using machine learning algorithms and historical data, IDCM can forecast future cooling needs and make proactive adjustments. This proactive approach helps avoid overcooling or undercooling, optimizing energy usage.
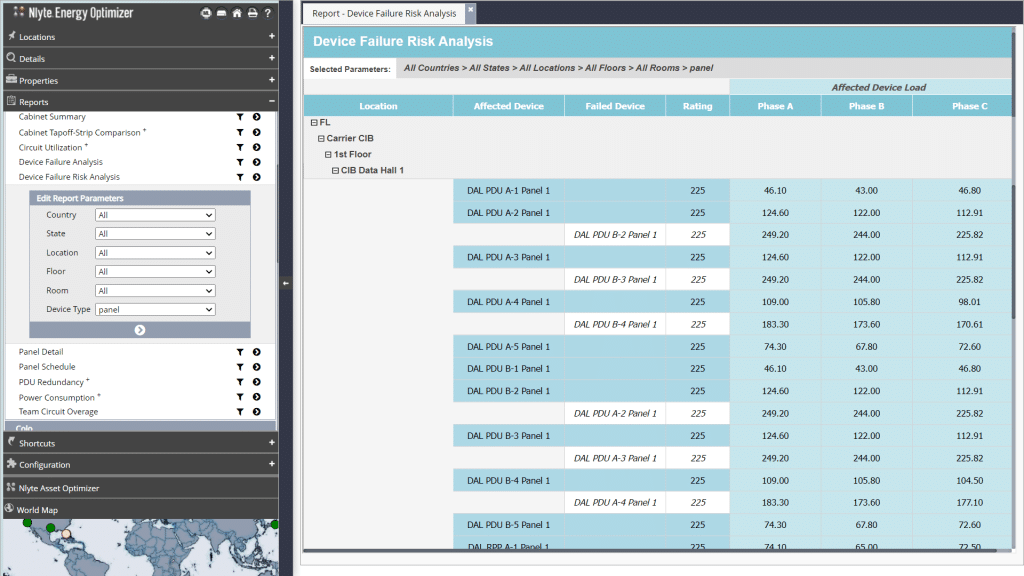
- Automation: IDCM systems can automate many processes, including cooling. Based on real-time and predictive data, these systems can autonomously adjust cooling systems to maintain optimal conditions, reducing the burden on operators and minimizing human error.
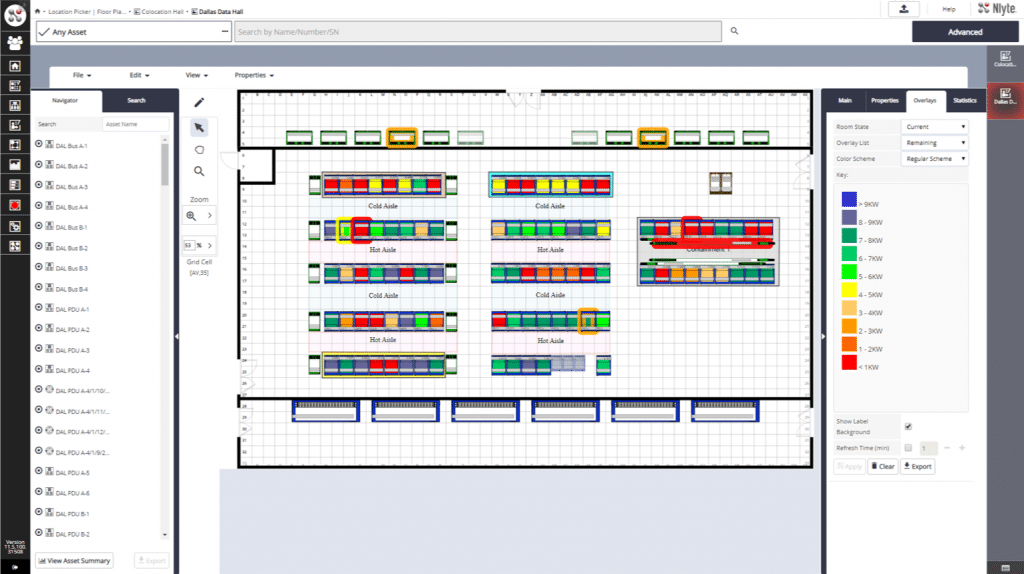
- Visualization: IDCM solutions often include visualization features that help operators to identify hotspots and optimize airflow and equipment placement. This can contribute significantly to improved cooling efficiency.
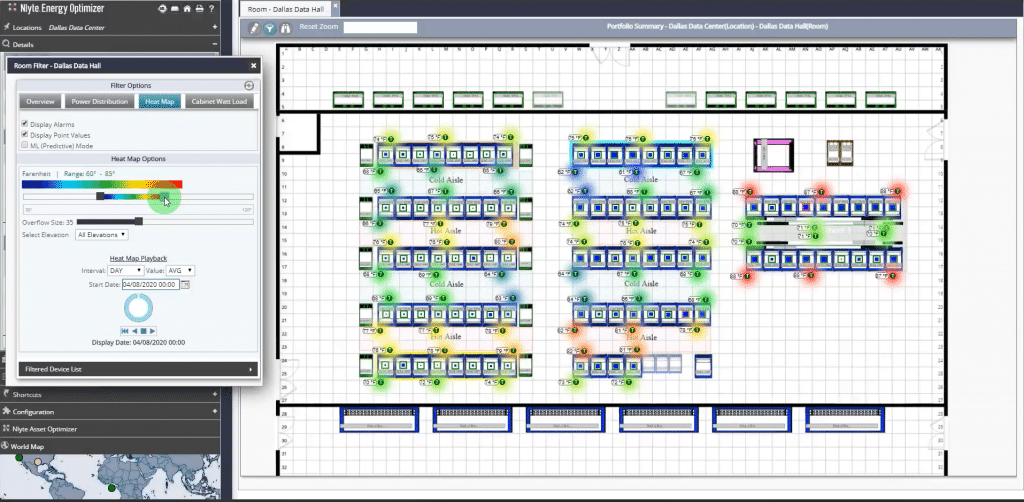
- Integration: An essential aspect of IDCM is its ability to integrate with other systems in the data center, from servers and storage to HVAC and security systems. This integration facilitates holistic management and optimization of data center operations.
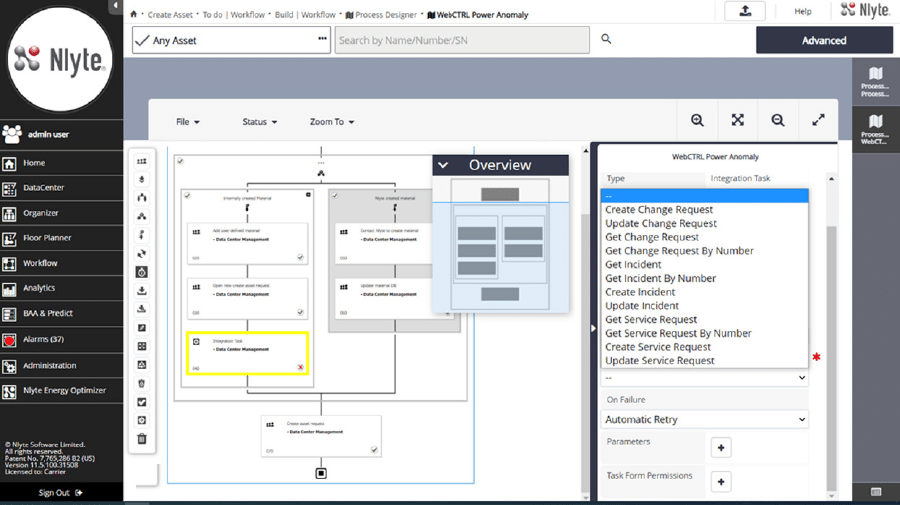
Benefits of Integrated Data Center Management:
- Improved cooling efficiency: By enabling precise control over cooling systems and providing insights into thermal conditions across the data center, IDCM can significantly enhance cooling efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
- Reduced costs: By optimizing cooling and other operations, IDCM can lead to substantial cost savings. It can also help avoid downtime and extend equipment lifespans, leading to further savings.
- Enhanced decision-making: With comprehensive, real-time data at their fingertips, data center operators can make more informed decisions and respond rapidly to changing conditions.
- Scalability: IDCM systems can easily scale with the growth of the data center, supporting efficient management as the complexity and size of operations increase.
Integrated Data Center Management (IDCM) represents a key strategy for improving cooling efficiency in data centers. By providing comprehensive control and visibility over operations, IDCM enables data center operators to optimize cooling, reduce energy consumption, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Additional information on IDCM
- Case Study: Sandia National Laboratories’ Holistic Data Center Design Integrates Energy and Water Efficiency, Flexibility, and Resilience case study
- eBook: IDCM for Dummies | Nlyte
- Streamlining Data Center Management: The Benefits of Integrated Data Center Management (IDCM) – AutomatedBuildings.com
- Driving Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Through Integration – AutomatedBuildings.com
- Integrating Building Automation System and Data Center Infrastructure Management System for Sustainable Data Centers | Nlyte
Liquid Immersion Cooling
Liquid immersion cooling is an innovative method that offers a highly efficient solution to cool down data centers. This technology involves submerging computer components or even entire servers in a non-conductive liquid that can absorb a large amount of heat.
There are primarily two types of liquid immersion cooling: single-phase and two-phase immersion cooling.
- Single-Phase Immersion Cooling: In this approach, the electronic components are submerged in a dielectric liquid that doesn't change its state when absorbing heat. The heat generated by the servers is directly transferred to the liquid, which then circulates and transfers the heat to a radiator or heat exchanger. The cooled liquid is then circulated back to continue the cooling process.
- Two-Phase Immersion Cooling: The servers are immersed in a special liquid that boils off when it absorbs heat from the servers. The vapor then condenses when it comes into contact with a cooled condenser coil. The liquid then drips back into the tank, where it repeats the process. This phase-change process is highly effective at removing heat.
Benefits of Liquid Immersion Cooling:
- Higher Efficiency: Liquid has a higher heat capacity than air, which means it can absorb and carry away more heat. This makes liquid immersion cooling significantly more efficient than traditional air cooling, resulting in substantial energy savings.
- Increased Density: Liquid cooling allows for higher server densities, as it removes heat more effectively. This can help reduce the physical footprint of data centers.
- Noise Reduction: As there are no fans required to circulate air, liquid immersion cooling can drastically reduce the noise levels within a data center.
- Less Maintenance: Immersion cooling systems generally require less maintenance than traditional cooling systems as they have fewer moving parts.
- Improved Hardware Lifespan: The liquid used in immersion cooling doesn’t produce moisture and minimizes oxidation, potentially extending the life of the hardware.
While liquid immersion cooling presents a promising solution to enhance cooling efficiency in data centers, it is essential to consider the challenges, including the need for specific server designs and changes in hardware maintenance procedures. However, as technology progresses and the demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions grows, it's expected that these obstacles will be overcome, making liquid immersion cooling a practical choice for more data centers.
Additional information on Liquid Immersion Cooling
- Direct liquid cooling: pressure is rising but constraints remain - Uptime Institute Blog
- An introduction to liquid cooling in the data center - DCD (datacenterdynamics.com)
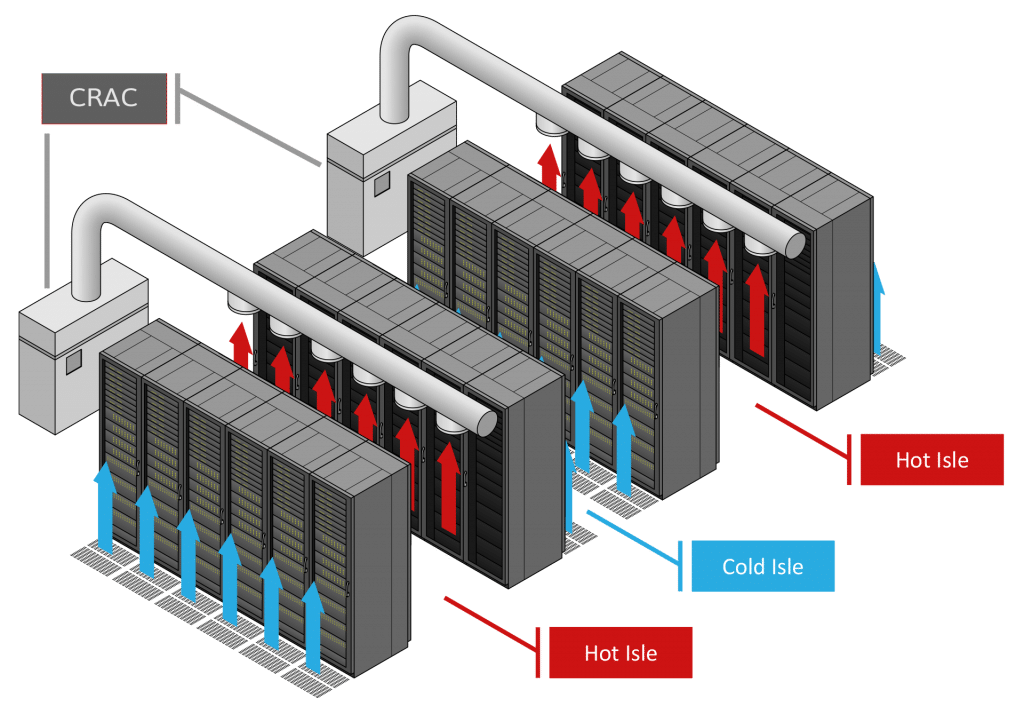
Heat Aisle Containment
Heat aisle containment is a method designed to increase cooling efficiency by segregating the hot exhaust air from the cold intake air in a data center. This process involves enclosing the hot aisles – the areas that take in the hot air expelled by server equipment – to prevent the mixing of hot and cold air.
There are two primary types of aisle containment systems: Hot Aisle Containment (HAC) and Cold Aisle Containment (CAC).
- Hot Aisle Containment (HAC): This method encapsulates the hot aisle, trapping the hot exhaust air from the servers and guiding it directly to the cooling units. This prevents the heated air from mixing with the cooled air, increasing overall cooling efficiency and creating a more predictable and manageable environment. The cold aisles remain open in this setup, ensuring cool air can freely reach server intakes.
- Cold Aisle Containment (CAC): Unlike HAC, this method involves enclosing the cold aisles, ensuring that the cool air produced by the air conditioning units is confined to the area where it's needed most - the server air intakes. This process helps to prevent the cool air from mixing with the warm air in the rest of the data center, increasing cooling efficiency.
Benefits of Heat Aisle Containment:
- Energy Efficiency: By separating hot and cold air, aisle containment minimizes the overcooling often necessary in uncontained data centers, leading to substantial energy savings.
- Increased Capacity: Containment can allow for higher server inlet temperatures, enabling cooling systems to operate more efficiently and freeing up additional cooling capacity.
- Improved Hardware Reliability: By providing a consistent, predictable airflow, containment reduces the risk of hot spots that could damage equipment and helps maintain a stable, optimal operating environment for servers.
- Scalability: Containment systems are scalable and can accommodate growth in data center infrastructure without major reconfiguration.
However, implementing aisle containment should be done carefully, considering factors such as fire safety regulations, room layout, and the existing cooling system setup. Despite these considerations, heat aisle containment stands as a proven method for improving data center cooling efficiency, and it continues to gain adoption as data centers seek to optimize their energy use.
AI and Machine Learning
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms can also play a significant role in improving cooling efficiency. These technologies can monitor and analyze various parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and airflow, and dynamically adjust the cooling system to maintain optimal conditions. Moreover, predictive analytics can help forecast future cooling needs based on historical data, ensuring proactive rather than reactive adjustments.
Implementing Green Building Design Principles
Data centers can incorporate green building design principles for better energy efficiency. This includes optimizing the building envelope, using energy-efficient windows, and integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar power. Additionally, using roof materials with high solar reflectance can reduce the amount of heat entering the data center, lowering the need for cooling.
Additional information on Green Building Design Principles
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
While it might seem basic, regular maintenance and cleaning of data center cooling systems can have a significant impact on their efficiency. Dust and other particles can clog filters and reduce airflow, making the systems work harder and consume more energy. Therefore, a routine cleaning and maintenance schedule is an essential aspect of efficient data center operation.
Conclusion
The continual advancement in technology and growing demand for data processing power are creating an increasing need for more powerful and efficient data centers. Cooling systems form a crucial aspect of data center operations, significantly impacting their energy efficiency, sustainability, and operational costs.
Techniques like heat aisle containment, liquid immersion cooling, advanced HVAC systems, and the use of AI and machine learning in cooling management are critical to enhancing efficiency. Additionally, regular maintenance, incorporating green building principles, and adopting integrated data center management (IDCM) tools further contribute to a comprehensive and efficient cooling strategy.
In this era of rapid digital expansion, embracing these multifaceted and innovative cooling strategies can significantly optimize data center operations, providing significant energy and cost savings, reducing environmental impact, and ensuring operational reliability. As data centers continue to evolve and grow, continuous innovation in cooling technologies and strategies will be the key to meeting future challenges. By combining technology, design, and smart management, data centers can become more sustainable and efficient, supporting the digital world's sustainable growth.
Additional Resources
- Data Center Sustainability Compliance Reporting
- Driving Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Through Integration - AutomatedBuildings.com
- Streamlining Data Center Management: The Benefits of Integrated Data Center Management (IDCM) – AutomatedBuildings.com
- Integrating Building Automation System and Data Center Infrastructure Management System for Sustainable Data Centers
- Standard 90.4: Energy Standard For Data Centers, February 2023 ASHRAE Journal
- Introduction to Integrated Data Center Management (IDCM) – YouTube
- Integrated Data Center Management | Nlyte
- Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) For Dummies | Nlyte
- Data Center Basics | Nlyte
- Integrated Data Center Management | Automated Logic
- Data Centers | Carrier Commercial Systems
- Data Center Solutions Brochure | Carrier Commercial Systems